DES
1. 개요
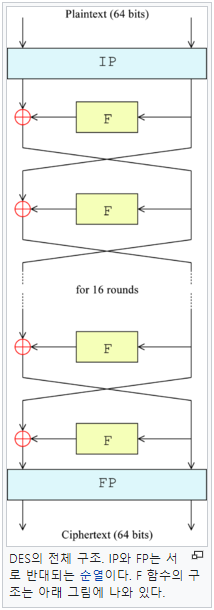
데이터 암호화 표준(Data Encryption Standard, DES)은 블록 암호의 일종으로, 미국 NBS (National Bureau of Standards, 현재 NIST)에서 국가 표준으로 정한 암호이다. DES는 대칭키 암호이며, 56비트의 키를 사용한다.
DES는 현재 취약한 것으로 알려져 있다. 56비트의 키 길이는 현재 컴퓨터 환경에 비해 너무 짧다는 것이 하나의 원인이며, DES에 백도어가 포함되어 있어 특수한 방법을 사용하면 정부 기관에서 쉽게 해독할 수 있을 것이라는 주장도 제기되었다.
1998년에 전자 프론티어 재단(EFF)에서는 56시간 안에 암호를 해독하는 무차별 대입 공격 하드웨어를 만들었으며, 1999년에는 22시간 15분 안에 해독하는 하드웨어를 만들었다.
DES를 세 번 반복해서 사용하는 Triple-DES는 DES에 비해 안전한 것으로 알려져 있으며, 또한 현재는 DES 대신 AES(Advanced Encryption Standard)가 새 표준으로 정해져 사용되고 있다.
2. 역사
1972년에 미국 NBS (National Bureau of Standards, 오늘날의 NIST)는 암호 기술의 필요성을 절감하고 미국 정부 규모의 표준적인 암호 알고리즘을 개발하기로 했다. 이에 1974년 8월 27일, IBM에서 루시퍼 암호 알고리즘을 제안했고, 이를 수정하여 1975년 3월 17일에 DES를 발표했다.
- DES 파이스텔 함수(F 함수)
- DES 전체 구조
- EFF에서 제작한 DES 무차별 대입 공격 하드웨어
3. 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class DESUtil {
private static Key key = null;
static {
if (key == null) {
// Key 초기화
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
try {
keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("TripleDES");
keyGenerator.init(168);
key = keyGenerator.generateKey();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static String encrypt(String inStr) {
StringBuffer sb = null;
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("TripleDES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
byte[] plaintext = inStr.getBytes("UTF8");
byte[] ciphertext = cipher.doFinal(plaintext);
sb = new StringBuffer(ciphertext.length * 2);
for (int i = 0; i < ciphertext.length; i++) {
String hex = "0" + Integer.toHexString(0xff & ciphertext[i]);
sb.append(hex.substring(hex.length() - 2));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static String decrypt(String inStr) {
String text = null;
try {
byte[] b = new byte[inStr.length() / 2];
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("TripleDES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(inStr.substring(2 * i, 2 * i + 2), 16);
}
byte[] decryptedText = cipher.doFinal(b);
text = new String(decryptedText, "UTF8");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return text;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DESUtil desUtil = new DESUtil();
String planText = "Hello World";
String encrtpt = desUtil.encrypt(planText);
String decrypt = decrypt(encrtpt);
System.out.println("DES 암호화 : " + encrtpt);
System.out.println("DES 복호화 : " + decrypt);
}
}
[출처 및 참고]
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.