HMAC
1. HMAC이란
암호학에서 HMAC(keyed-hash message authentication code, hash-based message authentication code)는 암호화 해시 함수와 기밀 암호화 키를 수반하는 특정한 유형의 메시지 인증 코드(MAC)이다. 여느 MAC처럼 메시지의 데이터 무결성과 진본 확인을 동시에 수행하기 위해 사용할 수 있다.
SHA-2, SHA-3 등의 암호화 해시 함수는 HMAC 연산을 위해 사용할 수 있다. 그 결과가 되는 MAC 알고리즘은 HMAC-X이며 여기서 X는 사용이 되는 해시 함수(예: HMAC-SHA256 또는 HMAC-SHA3-256)를 의미한다. HMAC의 암호화 등급은 그 기반이 되는 해시 함수의 암호화 등급, 해시 출력의 크기, 키의 크기와 품질에 따라 달라진다.
HMAC는 메시지를 암호화하지 않는다. 그 대신, 메시지의 암호화 여부에 관계없이 메시지는 HMAC 해시와 함께 송신되어야 한다. 기밀 키를 가진 쌍방은 스스로가 다시 메시지를 해싱하게 되며 진본인 경우 수신 후 연산 되는 해시가 일치하게 된다.
HMAC 구성의 정의와 분석은 1996년 Mihir Bellare, Ran Canetti, and Hugo Krawczyk의 논문에 처음 출간되었으며 이들은 1997년 RFC 2104를 작성하기도 했다. 또, 1996년 논문은 NMAC라는 내포형(nested) 변종을 정의하였다. FIPS PUB 198은 HMAC의 이용을 일반화하고 표준화한다. HMAC는 IPsec, SSH, TLS 프로토콜, 그리고 JSON 웹 토큰에 사용된다.
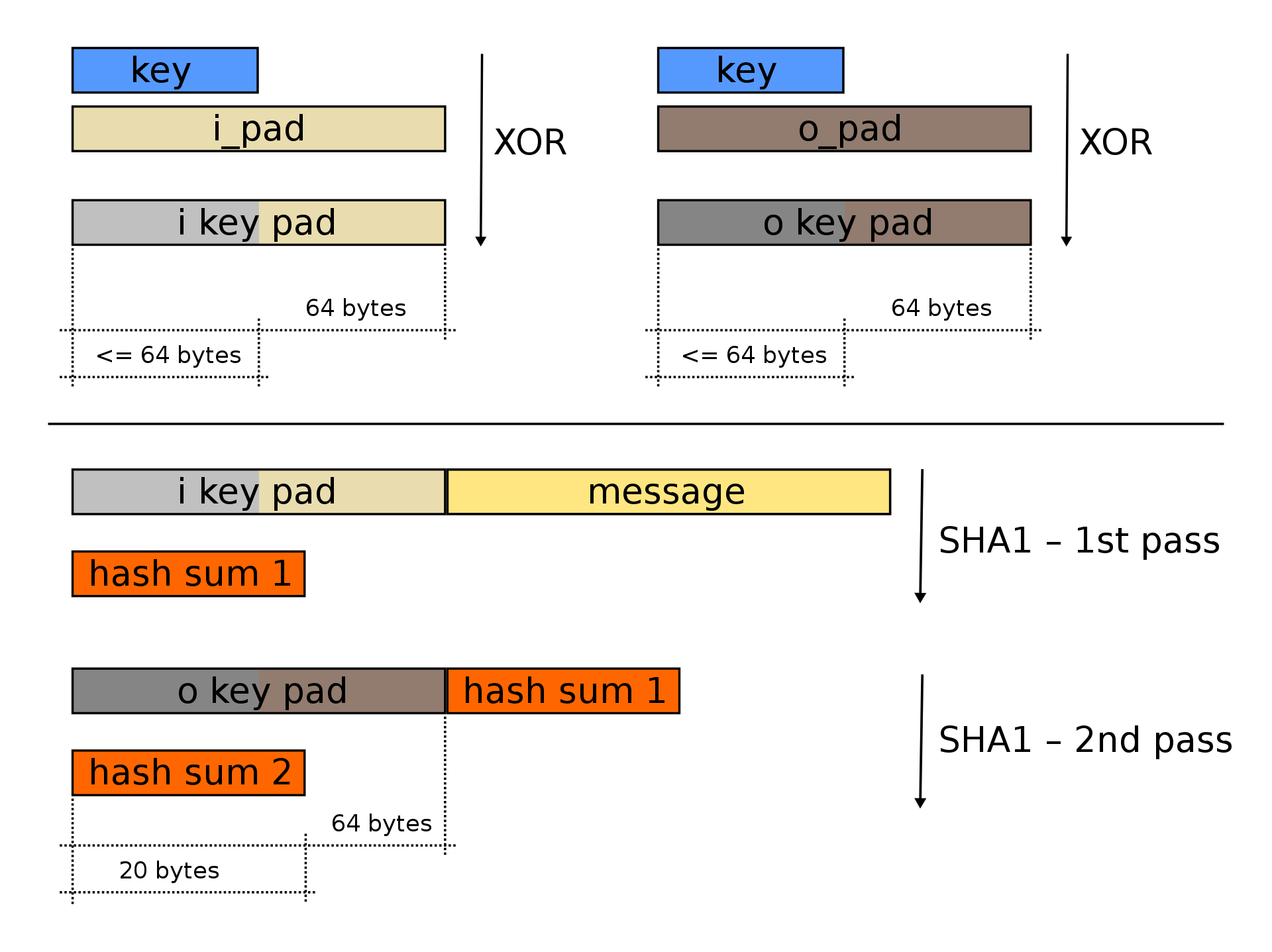
2. 동작 방식
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
function hmac is
input:
key: Bytes // Array of bytes
message: Bytes // Array of bytes to be hashed
hash: Function // The hash function to use (e.g. SHA-1)
blockSize: Integer // The block size of the hash function (e.g. 64 bytes for SHA-1)
outputSize: Integer // The output size of the hash function (e.g. 20 bytes for SHA-1)
// Keys longer than blockSize are shortened by hashing them
if (length(key) > blockSize) then
key ← hash(key) // key is outputSize bytes long
// Keys shorter than blockSize are padded to blockSize by padding with zeros on the right
if (length(key) < blockSize) then
key ← Pad(key, blockSize) // Pad key with zeros to make it blockSize bytes long
o_key_pad ← key xor [0x5c * blockSize] // Outer padded key
i_key_pad ← key xor [0x36 * blockSize] // Inner padded key
return hash(o_key_pad ∥ hash(i_key_pad ∥ message))
3. 안전한 사용
HMAC은 임의의 message와 secret key를 사용한 이중 해시 구조이므로 다른 입력값에 대해 같은 hash 값을 내는 해시 충돌에 대해 hash 알고리즘보다 훨씬 더 안전하다.
1) 전송시 HTTPS 사용
HMAC은 secret key가 없다면 message의 위변조가 불가능하지만, 원문 message를 같이 보내야 하므로 보안을 위해 HTTPS같이 안전한 전송 채널을 사용하여 전송해야 한다.
2) Secret key 관리
client가 전송한 요청은 중간에 해커가 가로챌 수 있지만, secret key가 없다면 위변조해도 서버의 검증 과정에서 에러가 나게 된다.
반대로 secret key가 유출된다면 해커가 임의로 위변조할 수 있음으로 secret key를 안전하게 관리하고 유출 우려가 있으면 재발급해서 사용해야 한다.
3) Replay attach 방지
client가 전송한 요청은 중간에 해커가 가로채서 replay attack 에 활용할 수 있다. 그래서 전송 message 에 timestamp나 serial, nonce 등 변하는 값을 포함하는게 필요하다.
4. 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class HMacTest {
public static final String ALGORITHM = "HmacSHA256";
public static String calculateHMac(String key, String data) throws Exception {
Mac sha256_HMAC = Mac.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
SecretKeySpec secret_key = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes("UTF-8"), ALGORITHM);
sha256_HMAC.init(secret_key);
return byteArrayToHex(sha256_HMAC.doFinal(data.getBytes("UTF-8")));
}
public static String byteArrayToHex(byte[] a) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(a.length * 2);
for(byte b: a)
sb.append(String.format("%02x", b));
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception {
// see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMAC#Examples
// expected output:
// HMAC_SHA256("key", "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog") = f7bc83f430538424b13298e6aa6fb143ef4d59a14946175997479dbc2d1a3cd8
System.out.println(calculateHMac("key", "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"));
}
}