Java Stack
1. Stack
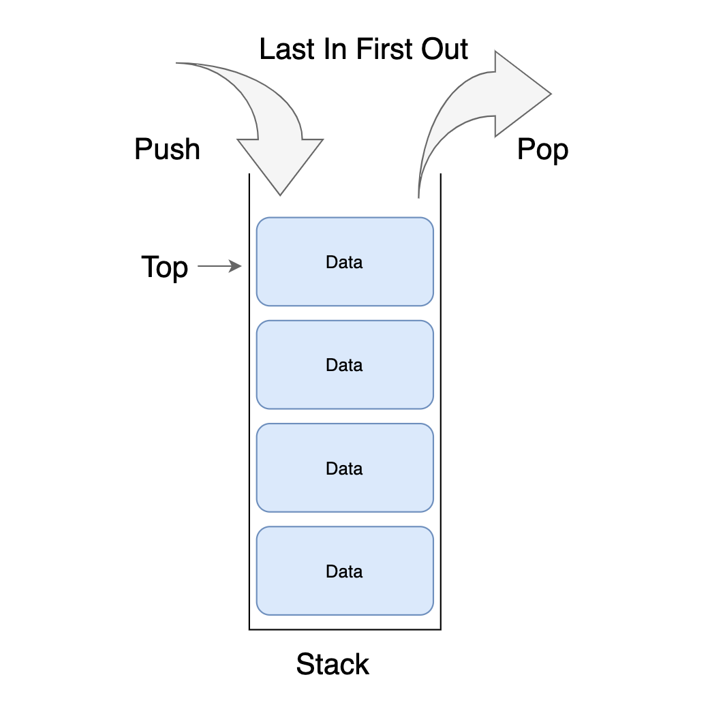
스택(Stack)의 사전적 정의는 ‘쌓다’, ‘더미’로서 상자에 물건을 쌓아 올리듯이 데이터를 쌓는 자료구조이다.
스택은 가장 나중에 들어온 데이터가 가장 먼저 빠져나가는 후입선출(LIFO : Last In First Out) 구조로 되어 있어, 데이터가 입력된 순서대로 처리되는 것이 아니라 나중에 들어온 데이터를 먼저 처리할 때 사용한다.
2. 선언
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer 스택 선언
Stack<Integer> intStk = new Stack<>();
// String 스택 선언
Stack<String> strStk = new Stack<>();
// Boolean 스택 선언
Stack<Boolean> bolStk = new Stack<>();
}
}
3. 메서드
1) push()
데이터를 스택에 추가하고 해당 값을 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> intStk = new Stack<>();
intStk.push(1);
intStk.push(2);
intStk.push(3);
System.out.println(intStk);
}
}
2) pop()
스택의 마지막 요소를 제거하고 해당 값을 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> intStk = new Stack<>();
intStk.push(1);
intStk.push(2);
intStk.push(3);
System.out.println(intStk.pop());
}
}
3) peek()
스택의 마지막 요소를 반환하며, 스택에는 변화를 주지 않는다. 스택이 비어있을 경우 NoSuchElementException이 발생한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> intStk = new Stack<>();
intStk.push(1);
intStk.push(2);
intStk.push(3);
System.out.println(intStk.peek());
}
}
4) empty()
스택이 비어있는지 여부를 반환한다. 비어있는 경우 true, 비어있지 않는 경우 false를 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> intStk = new Stack<>();
System.out.println(intStk.isEmpty());
intStk.push(1);
intStk.push(2);
intStk.push(3);
System.out.println(intStk.isEmpty());
}
}
5) search()
메서드의 인자를 스택에서 검색하여 해당 위치를 반환한다. 만약 해당 인자가 여러 개일 경우, 마지막 위치를 반환한다.
위치는 인덱스가 아닌 빠져나오는 순서이다. 찾는 값이 스택에 없을 경우 -1을 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> intStk = new Stack<>();
intStk.push(1);
intStk.push(2);
intStk.push(3);
System.out.println(intStk.search(2));
System.out.println(intStk.search(1));
System.out.println(intStk.search(4));
}
}
[출처 및 참고]
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.